Technical solutions for green control of vegetable pests
WeChat counseling

Scan the QRCode and add my wechat
2024-11-05 17:25 Source: Rui Feng Number of hits: 495

1. Monitoring and early warning of pests and diseases
According to the characteristics and rules of occurrence of vegetable diseases and insects, systematic monitoring of vegetable diseases and pests should be carried out, the occurrence and development of diseases and insects should be timely and comprehensively grasped, and the monitoring and early warning information of diseases and insects should be accurately released to provide scientific basis for unified prevention and control.
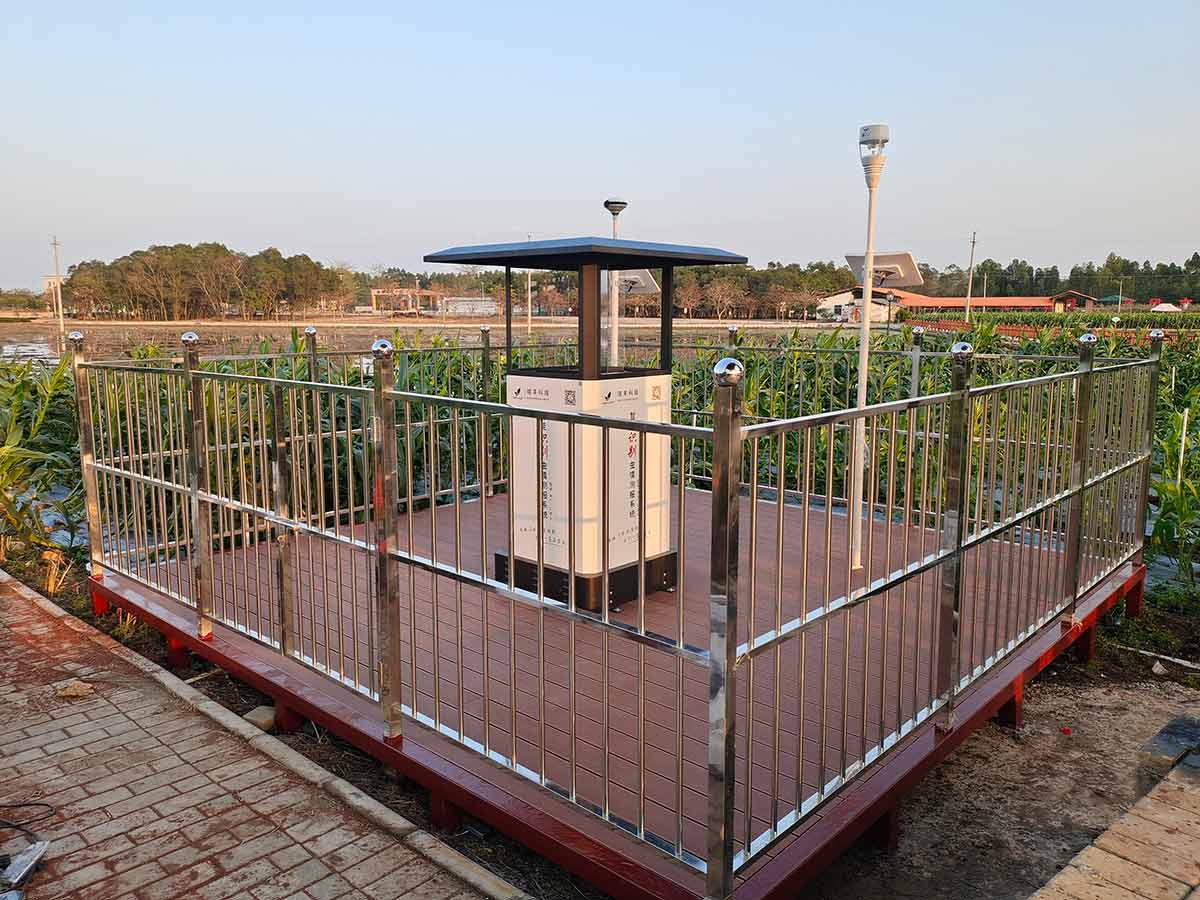

In the demonstration area, representative fruit and vegetable crops were selected, and a multi-functional pest trap and intelligent pest identification and reporting system were installed to monitor the occurrence of xylostoma, Callostoma, Beet moth, tiger, pod borer, bean borer, melon fly, flannelia flannelaria and other pests, and to learn the occurrence of these pests in the field remotely and in real time. At the same time, it can also collect the climate factors including temperature, humidity and rainfall in the park in real time to provide scientific basis for prevention and control.
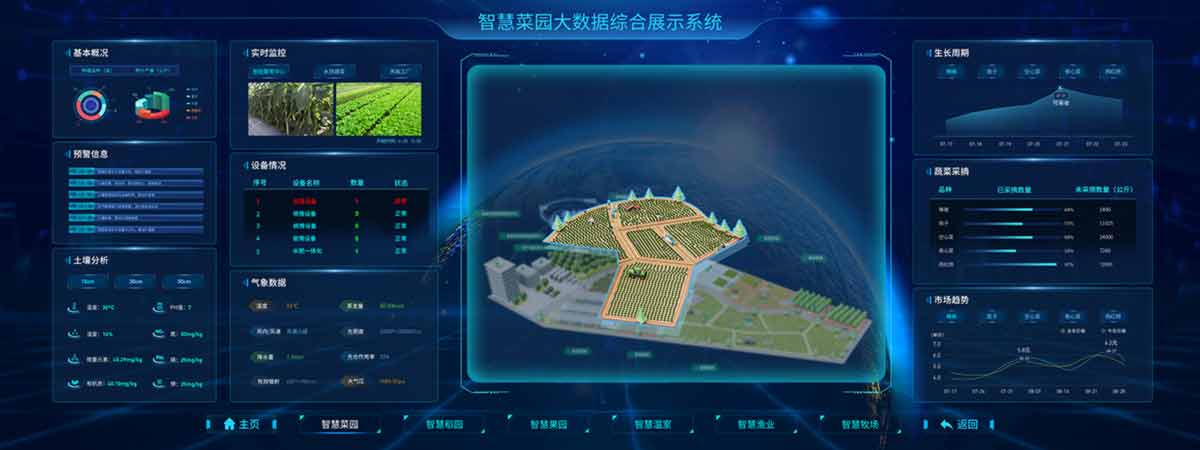
2. ecological regulation
Through cultivation and management measures, optimize the environmental conditions of vegetable growth and development, promote the robust growth of vegetables and improve the stress resistance of vegetables; The environmental conditions for the propagation and spread of diseases and pests shall be worsened, and the breeding and spread of diseases and pests shall be controlled.
(1) Crop rotation. Through different crop rotation, the living environment of diseases and pests is changed, and the associated relationship between pests and vegetables is destroyed.
(2) Cultivate strong seedlings. Choose large, full seeds and nutrient-rich soil or substrate to grow seedlings, so that vegetables are vulnerable to pests and diseases to avoid the reproduction and diffusion peak, so as to avoid or reduce the damage of pests and diseases.
(3) The selection of disease-resistant (tolerant) varieties. According to the occurrence of diseases and pests in local production, the excellent varieties with strong resistance should be selected accordingly, and the good disease resistance of vegetables should be fully applied to improve the resistance of vegetables to diseases and insects.
3. physical prevention
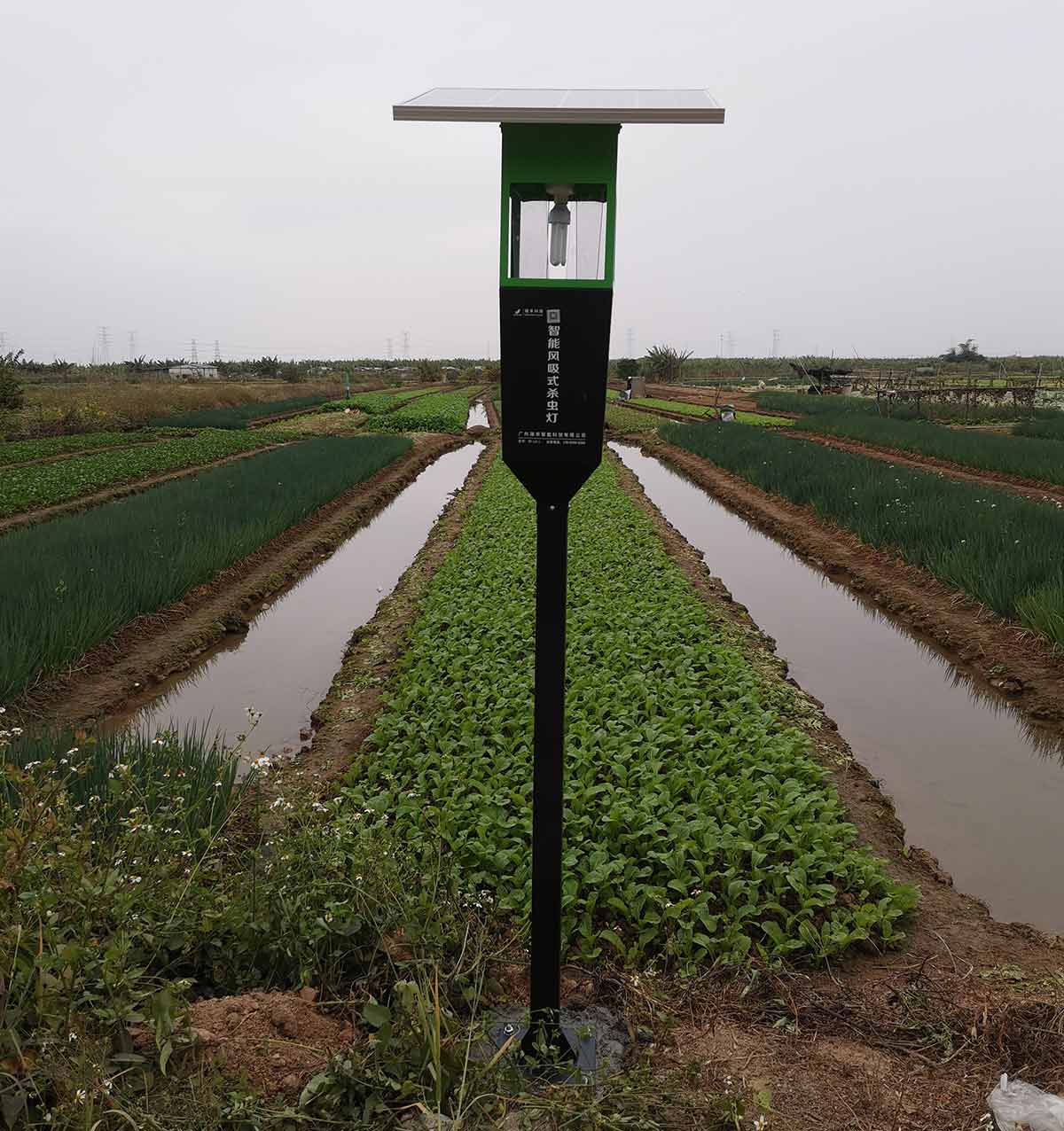
(1) insecticidal lamp trapping.
Using the phototaxis of the insect pests, the intelligent wind suction solar insect killing lamp was used to trap and kill the insect pests. Under the premise of enclosure, the purple fluorescence of the germicidal lamp was used to kill the bacteria. An insecticidal lamp is installed every 20-30 mu, and the lamp is turned on at night during the occurrence period of adult pests. The insecticidal lamp mainly traps vegetable pests such as Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, orthoptera, Homoptera, etc. The target pests of the trap include Diamond-moth, beet moth, Trichoplakia, cottonworm, tobacco worm, small ground tiger, and cockbeetle.

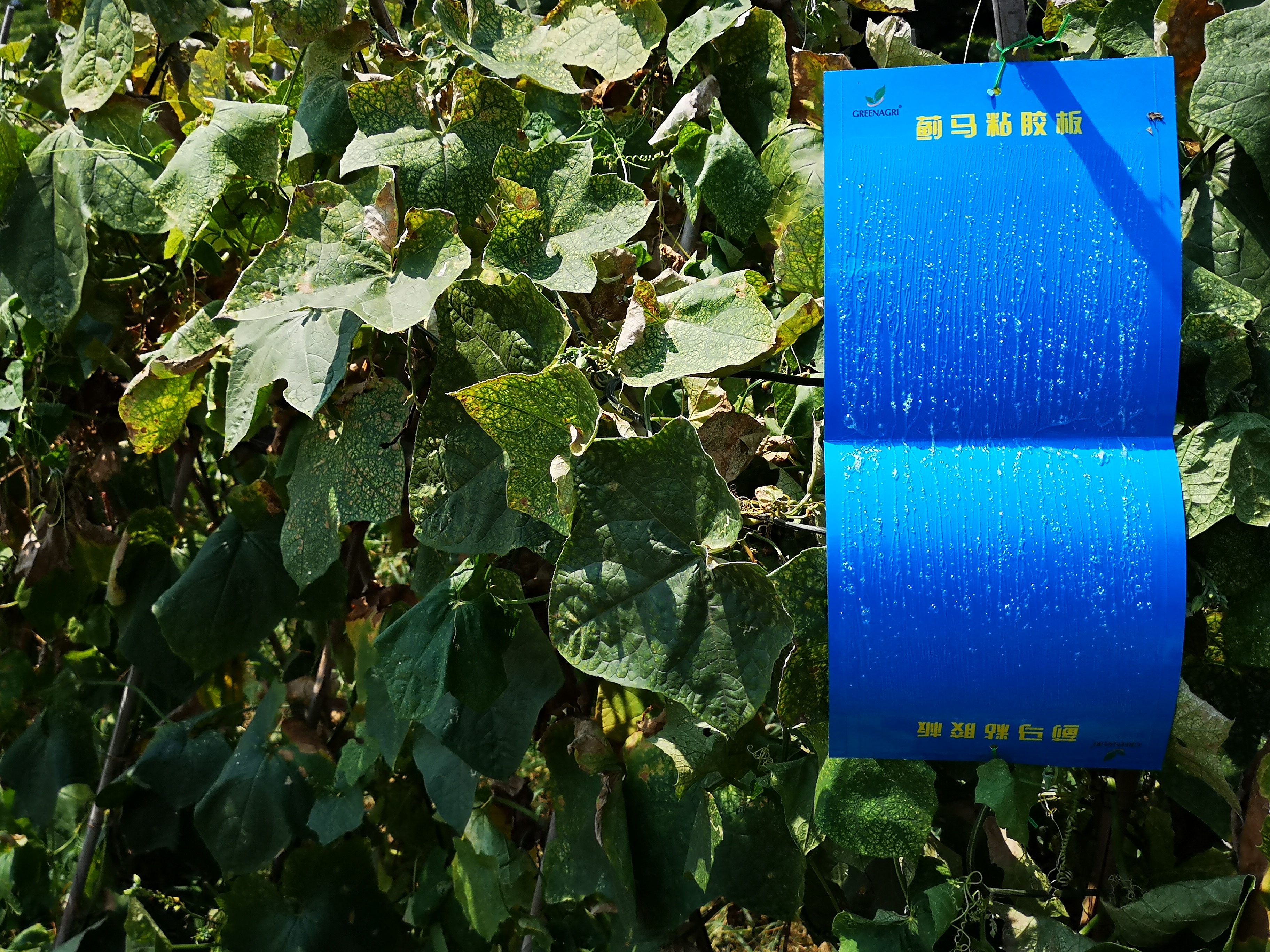
(2) Color plate trapping.
Using the color taxis of pests, the biodegradable pheromone armyworm plate (yellow plate/blue plate) was used to trap and kill small insects, such as flavistracula, macularia, winged aphis, whiteflies, thrips and so on.
(1) Yellow plate insect lure: According to the crop planting and insect quantity in the demonstration area, yellow plate is placed to trap and kill yellow insect pests such as yellow Curricola, spotted miner, winged aphid, whitefly, and diamond-moth, generally 20-40 pieces are inserted per mu, and the yellow plate should be 10-20cm higher than the top of the crop.

(2) Blue board (Thrips sticky board) : According to the crop planting and insect quantity in the demonstration area, blue board (thrips sticky board) is placed to trap and kill thrips, seed flies and other pests, generally 20-40 pieces per mu.

(3) Pheromone trapping.
According to the crop planting types and the local occurrence rules of target pests, the application time of sex attractants was determined and adjusted. The use of sex attractants began at the early stage of pest occurrence and when the insect population density was low. At the same time, the occurrence rules of target pests in the field could be monitored by pheromone trapping. Commonly used insect traps include: Diamond-moth, Litterworm, beet moth, cotton bollworm, melon fly, bean pod borer, bean wild borer, small ground tiger, etc.
4. Biological control
(1) Protection and utilization of natural enemies: planting nectar plants around vegetable fields provides shelter and food for natural enemies, and improves the natural control effect of natural enemies.
(2) Release of natural enemies:
To control lepidopteran pests such as Lepidopteran, Beet moth and Diamond-moth in the field; Using the technique of "treating mites with mites", the predatory mites were released in the field to control the harmful mites such as red spider. In the vegetable growing area of the facility, harlequins and lacewings can be released to control aphids.

5. Scientific drug use
(1) biopesticide control: When it is necessary to use pharmaceutical control, priority should be given to biopesticides, such as natural pyrethrin, rotenone, Beauveria bassiana, cetosaine, Bt and NPV, polyamycin or primomycin, and other biological agents such as oligomycin.
(2) Chemical pesticide prevention and control: When the occurrence of diseases and insects still exceeds the control index after the use of comprehensive measures, reasonable use of high-efficiency, low-toxicity and low-residue chemical pesticides for emergency prevention and control.


Scan the QRCode and add my wechat
We will provide you with professional product support and after-sales service.
Telephone 09:00-18:00
020-85286020